Electrostatics in Industry
How it is generated and what you can do about it
Below we describe how the charge is generated. It explains the way that occurs most often in industry: electron displacement by contact and separation. There are other possibilities such as strong radiation, influenza etc. We will not go into this.
...leads to permanent static charge creation
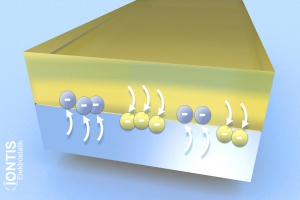
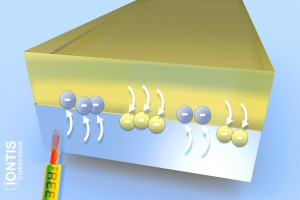
 During the separation process, depending on the (separation) speed, electrons cannot return but are “torn away”.
During the separation process, depending on the (separation) speed, electrons cannot return but are “torn away”.
As a result, an electron is missing in one place, while it is too much in the overall balance at the new place: positive AND negative charge islands arise, regardless of whether a substance is conductive or not.
Charge does not flow off: electrostatic
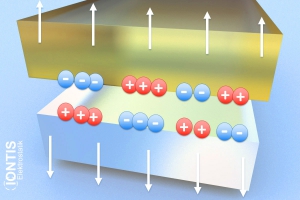
 An insulator is neither through the material…
An insulator is neither through the material…
…nor dissipative on / over the surface i.e. the charge does not flow off and remains.
The electrical charge remains in place, i.e. is static -> electrostatic
Grounding is useless.
The effect of grounded machine parts
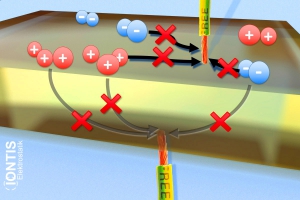
 As with all materials, also with conductive and grounded materials an electron transfer to electrostatic equilibrium takes place at the contact surfaces.
As with all materials, also with conductive and grounded materials an electron transfer to electrostatic equilibrium takes place at the contact surfaces.
Depending on the speed, electrons are also left behind during the separation process.
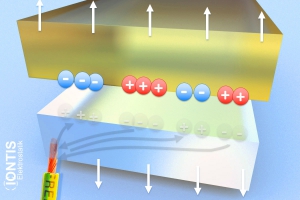 While an insulator (upside) remains charged, the conductive body (below) e.g. metal roller can simply discharge towards earth.
While an insulator (upside) remains charged, the conductive body (below) e.g. metal roller can simply discharge towards earth.
But electrostatic charge at the insulator (top) e.g. plastic foil is not avoided -> dissipative and grounded machine parts do not prevent electrostatic charge on the material!
Remedy: Charge neutralisation through active discharge
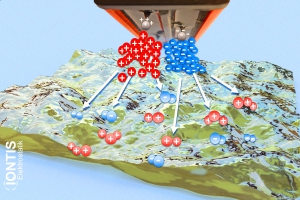 Air molecules are charged with antistatic bars: high voltage is applied to sharp tips, which ionises the air, i.e. the air picks up the charge.
Air molecules are charged with antistatic bars: high voltage is applied to sharp tips, which ionises the air, i.e. the air picks up the charge.
The ions are attracted by the opposite charge on the material surface and migrate there (up to 1500mm without additional air support).
The air exchanges the charge on the surface and neutralises the surface almost completely.
The ionization takes place in a pulsed manner – plus and minus are never generated simultaneously, but are clocked.
No surface is really smooth, but the air molecules reach “mountain and valley”.
Reduction but not neutralisation: Passive Ionisers
 In passive systems like antistatic brushes, many mandatory grounded fiber tips are brought very close to the material and also work with ionised air.
In passive systems like antistatic brushes, many mandatory grounded fiber tips are brought very close to the material and also work with ionised air.
The passive ionisers discharge the material through a very narrow air gap due to the electric field, which builds up naturally against earth.
However, this physical effect breaks off at a certain field strength, as a consequence a passive ionizer does not reach a low residual charge, we are not talking about neutralisation here. The discharge is just enough to avoid sparks and shocks to operators, but rarely to avoid adhesion (e.g. dirt, other materials etc.) or repulsion (e.g. ink droplet misprinting or telescoping of foil).
IONTIS Elektrostatik GmbH
Friedrich-Rottra-Str. 66
D-79588 Efringen-Kirchen
- Tel. +49 7628 35 94 064
- Fax +49 7628 35 94 065
- mail@iontis.de